The need for parallel operation is to share the load when demand for higher power rating is very high in the bus bar lines
The bus bar is made up of thick copper wire. rather than one single higher power rating dc generation, the small dc machines are operated is parallel. Because of maintain and repairs, continuous power supply.
Conditions for parallel operation
- The terminal voltage of incoming dc generator should be equal to the bus bar voltage.
- The polarity of bus bar should be matched with the polarity of dc generator.
- The prime mover speed should be same for all the machine connecting in parallel.
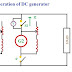
Consider the dc shunt generators G1 and G2 are connected to bus bars. The switches S and S1 are closed. Initially, the shunt generator G2 switches S' and S2 are open.
The G2 is to be connected to the bus bars to share the part load of G1. The generator G2 is run at rated speed by prime movers connected to G2. The switch S' is closed between negative terminal of bus bar and generator G2.
The voltage of G2 is varied by shunt field rheostat there by varying the field current.
The shunt field rheostat is adjusted such that, the voltmeter reads zero voltage for parallel operation.
The switch S2 is closed. In this condition, the induced emf in generator G2 is exactly equal to the bar voltage and there is no current flow through G2. This condition is called as floating generator.
The field current of generator G2 is increased, there by current I2 is flowing through bus bars. Likewise, the field current of generator is decreased, current I1 is flow through bus bars. The total current in the load is IL.
IL = I1 + I2
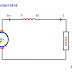
Load Sharing
The values of equal voltage intervals up to rated voltage and armature current are obtained. So, We can plot the drooped characteristics of generator G1 and G2.
The combined characteristics of two dc generators.
The two generators divide the load depends on dropping characteristics of each generator.
E1,E2 - Generated voltage of G1 and G2.
R1,R2 - Armature resistance
V- terminal voltage
problems on parallel operation of dc generators
for example, two shunt generator operating is parallel output current of 600 A
Generator G1, Armature resistance Ra1 is 0.02 ohm and Generated voltage E1 = 455v
Generator G2, Armature resistance Ra2 is 0.025 ohm and Generated voltage E2 = 460v
Find out terminal voltage and output power of each dc machine.
I1 + I2 = 600
(E1 - v)/Ra1 + (E1-v)/Ra2 = 600
E1= v + I1 Ra1
455 = v + I1 00.2
E1 = v + I2 Ra2
460 = v + (600-I1)0.025
By solving these two equation,
I1 = 222.2.2A
I2 = 377.77A
v = 450.56
output power of generator G1
P1=V*I1=100.12KW
output power of generator G2
P2=V*I2=170.2KW





0 Comments: